Understanding Power Quality |
In the recent years, both of the electric utilities and end users of electric power are becoming increasingly concerned about the quality of electric power.
The reason is that newest generation load equipments, with microprocessor-based controls and electronics devices, are more sensitive to power quality variations than were equipments used in the past.
The footprint of the new generation of electrical equipment gets smaller and smaller, that means less space between adjacent conductors on the circuit board, which increase in turn the susceptibility for over Voltage (even at low level), and increasing adjacent-channel interferences. The microprocessor chips also become smaller and smaller and more densely packed (more solid-sate components). This decreases heat dissipations, and makes them less robust. Moreover, the operating Voltage has and continuous to decrease, digital “1” maybe in the vicinity of 3.5-5.0 Volts or less, and “0” in the range of 0-1.5 Volts. Hence, smaller over Voltages from transient conditions may result in operating errors. Moreover, a zero reference Voltage (Clean Ground reference) is very critical for proper operations of computer-based equipments.
Also operating speeds have been increased (in the radio frequency range), making the circuit boards more sensitive to electromagnetic interferences.
Therefore, end users have an increased awareness of power quality issues more than anytime before, because it can have a direct economic impact on their critical equipments performance, and that impose extra responsibility on the end user to be aware from the invisible danger lurking their critical equipments.
In order to choose the right solution, one needs to know more about the electrical disturbances in general. Electrical disturbances are nothing more than electrical power in an unusable or undesirable form. Hence, plugging your sensitive equipments directly to the AC commercial power system expose it to all kinds of disturbances. For instance, over voltage, voltage drop, spikes, normal & common mode noise, EMI, RFI, etc.
Power line filters (like online UPS), eliminate disturbances (noise, spikes and transients) in the mains supply before they have a chance to damage your equipment, or affect their function, hence it maintains a pollution free electrical environment for your sensitive equipments to operate smoothly away from all types of the power line disturbances.
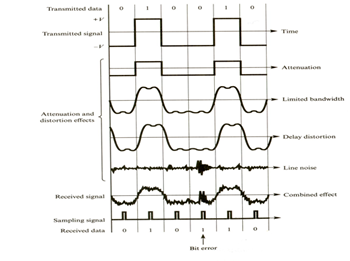
Normal mode noise is a noise potential between line and neutral, while Common mode noise is noise potential between Line and Neutral as pair and ground. Normal mode noise has negative impact on the hardware, while the common mode noise can disrupt the software.
Its well known that, computer-based equipments use ground as reference point; hence common mode noise represents big threat for them. They are directly or capacitively coupled into system logic reference ground. Even if 0.5 Volt of noise gets its way into this reference ground bus can shift that reference point momentarily causing disruption, as shown in the simulation diagram below: |
| |
 |
| |
Therefore, power demands of sensitive equipments require uninterrupted and high quality input power. Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and active filters provide this delivery. In terms of UPS systems, there are three major topologies that are used, as explained below: |
| |
Online Double Conversion Technology |
An uninterruptible power supply using true online double conversion technology provides the highest level of power protection available. The Online UPS converts the 230V input AC mains supply to DC power, which is then used to charge the battery. The DC current flow is then fed through an inverter stage that reconstructs the 230V AC mains output. Because the AC output is completely regenerated, it will be completely free from any mains-borne interference such as spikes, sags, swells, harmonic distortion, and noise. The output voltage and frequency is controlled precisely, thus ensuring a clean and stable sine wave power output.
Online UPS systems are able to withstand large fluctuations on the input voltage before transferring to battery power (typically 185V-275V) thus eliminating unnecessary battery discharges. Upon mains failure, transfer to battery power is seamless - no break.
Online UPS systems also have various failsafe and self-diagnostic features that will instantly transfer the load onto mains power if there is a failure within the UPS hardware or if the UPS is overloaded (internal solid sate bypass). Advantages of the online UPS systems are: |
| |
- Continuous & total power conditioning.
- Failsafe/overload protection with static bypass facility.
- No break on mains failure (zero switching time).
- Wide input voltage tolerance.
|
| |
While, the disadvantage is that the online UPS systems are more expensive than other types of UPS technologies. |
| |
Offline Standby Technology |
During normal operation of an, the power flows straight through the unit and hence only RFI filtering is usually provided. When the input voltage fails or fluctuates outside of a pre-set tolerance window, the UPS detects this and a relay will close, allowing the UPS to start feedingpower via the inverter.
The inverter is then switched on and a square, step or sine wave form output is supplied. Upon the return of mains power, the output is switched back onto mains and the inverter is turned off. Typically there will be a break of around 4 ms during the transfer to and from the battery mode. Advantages of Offline UPS systems are: |
| |
- Low cost
- Silent operation when in standby mode
- High efficieny
The disadvantages are:
- Limited power protection - only protects against a small percentage of problems of input power.
- Poor output voltage regulation - sags and surges will be passed straight to the load. Moreover, the output voltage waveform during battery backup mode will be square (not suitable for some loads).
- Break transfer to battery mode (around 4msec switching time).
- No fail-safe, that’s mean, UPS will drop the load if there is a high start-up current, overload or inverter failure.
|
| |
Line-Interactive Technology |
| |
Aline-interactive UPS operates in a very similar fashion to an offline UPS, except with the advantage of better filtering and output voltage boost/reduce features. While not eliminating mains-borne interference, line-interactive technologies reduce the impact of spikes, surges and sags by 'clipping' the peaks and valleys, boosting power or switching to battery back up.
As with offline UPS, when the input voltage fails or fluctuates outside of a pre-set tolerance window, the UPS detects this and a relay will close allowing the UPS to start feeding battery power via the inverter. The inverter, in a good line-interactive UPS, will supply a sine wave output. Upon the return of mains power, the output is switched back onto mains and the inverter is turned off.
As with offline UPS, typically there will be a break on the transfer to and from battery mode, though usually this will be shorter than with an offline UPS. Advantages of the line interactive UPS systems are: |
| |
- Lower cost than online UPS systems.
- Provide higher protection than offline UPS systems.
- Silent operation when in standby
- High efficiency
|
| |
The disadvantages are: |
- Fluctuations, such as spikes, noise, and harmonic distortion can still be passed straight to the load.
- Break on transfer to battery mode.
- No fail-safe, that means, UPS will drop the load if there is a high start-up current, overload or inverter failure (No internal bypass function).
|
| |
Generator & UPS Compatibility |
Due to the nature of the supply from aGenerator we recommend utilizing Online Double Conversion Technology UPS. Online UPS have improved input frequency and voltage tolerance over non-online technology, therefore preventing frequent switching to battery power which maximizes battery life and UPS reliability. Because Online Double Conversion Technology completely regenerates the AC output it will be completely free from interference such as spikes, noise, and harmonic distortion, which may adversely affect IT or other types of sensitive equipment.
Non-online UPS systems will often work, although intermittently, with a Generator supply but will ultimately fail. Usually the UPS failure happens under load or when the Generator is providing the main supply. A Generator backed supply is often a critical one and necessitates the highest form of protection, Online Double Conversion Technology provides this protection.
Preventative Maintenance saves time and money, and avoids unpleasant surprises. All UPS units include wearable parts. As such, they should be maintained on a routine basis. A properly maintained UPS will rarely, if ever, fail, thus making sure that it provides an uninterruptible supply of power at all times. Our factory- trained & certified Service Engineers are able to support and maintain your UPS equipment and clean power solution to the highest standards to ensure maximum uptime for your critical systems, data and operations.
When a UPS system needs to be integrated with standby generator, special attention is needed for the generator sizing issue, where some times 3:1 sizing ratio is needed. For professional advice, you can consult Babylon Power Solution project management team. |


